MenuMenu
- Compare. Save. Ship.
- Main Menu
- How It Works?
- Shipping Services
- eCommerce
- Learn

|
Table of Contents: |
For retailers, the accuracy and security of inventory is paramount. Knowing where your products are, and being able to quickly account for them, is crucial to protecting your bottom line. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is an excellent way for businesses to manage their inventory; it’s why the use of RFID in logistics is favored by companies of all industries and sizes.
“RFID tags give businesses real visibility over where their products are and gives amazing insight across every link of their supply chain. It also gives warehouse and shipping personnel easy, instant access to the essential information they need for accurate, timely shipping”
While RFID technology isn’t new, recent innovations of the technology are making impressive impacts throughout the logistics industry, such as improving shipping/picking accuracy rates by 80%.
In this article we’ll explain what RFID technology is, explore the role RFID has in modern logistics, and discuss the different types of RFID tags common in today’s supply chain logistics.
At its core, RFID is a sophisticated technology designed to track and manage items using radio waves.
This system comprises tags, which store data about the item they're attached to, and readers, which collect this information wirelessly. It's a step beyond traditional barcodes, offering real-time data without needing a line of sight.
Information that is stored in an RFID tag often includes:
RFID's ability to streamline inventory and asset tracking makes it indispensable in modern logistics, providing businesses with unparalleled visibility and control over their operations.
The ability of RFID to improve and streamline logistics operations is essential. Let’s take a look at how RFID is relied upon by logistics professionals.
RFID truly is a game-changer for inventory and asset tracking as it enables businesses to automatically monitor the whereabouts and status of their goods in real time.
Additionally, because RFID readers can read tags without requiring a direct line of sight with the tag, it enables multiple items to be tracked simultaneously, increasing inventory tracking speed and accuracy.
Without RFID and other visibility-enabling technologies, it’s not uncommon for retailers to not know the whereabouts of their assets and purchased inventory. However, by incorporating RFID solutions into a company’s logistics processes, inventory whereabouts can be easily identified with great accuracy.
Depending on the type of RFID tag being used, logistics teams can easily track an item from several feet away from the tagged item. This means large numbers of products can be instantly identified and tracked without requiring a person to visually identify and scan each item, freeing up valuable labor hours.
“Shrinkage,” or product loss, is a common experience of retailers within their logistics operations. An acceptable warehouse shrinkage rate is below 1.5%, with many 3PL warehouses having numbers both higher and lower than that.
RFID technology enables retailers to keep close tabs on products. This visibility helps keep a company’s shrinkage loss well below the average, potentially saving a company thousands of dollars in lost product.

Getting products onto the shelves of big retailers can be very beneficial for small businesses. However, there are many requirements that must be met before they can access shelf space, such as including RFID tags on all packaging before it reaches their warehouse.
For instance, in 2022 Wal-Mart implemented their RFID mandate, requiring suppliers of toys, sporting goods, housewares, and other products, to outfit packages with a UHF RFID tag.
RFID technology has become central to managing supply chain logistics effectively and efficiently. From tracking large shipping containers on cargo ships to clothing items in a store room, RFID is helping improve logistics at every level of the supply chain. There are numerous types of RFID tags, each one is designed for use in different situations and environments.
Passive RFID tags are a cornerstone of supply chain management, operating without their own power source and relying on the electromagnetic energy from RFID readers for activation. These are the rectangular stickers commonly found on products in stores.
These tags are cost-effective and durable, making them ideal for tracking items over their lifecycle. Industries like retail, manufacturing, and logistics heavily rely on passive tags.
Common uses of passive RFID tags include:
Active RFID tags are equipped with their own power source, enabling them to transmit signals over greater distances than passive RFID tags. This capability makes them ideal for tracking high-value assets and for applications requiring real-time monitoring.
Industries such as logistics, healthcare, and manufacturing utilize active RFID to enhance visibility and efficiency in asset management and supply chain operations.
For example, in logistics, active RFID tags are used to track shipping containers across global supply chains, providing real-time location data and significantly improving the management of goods from origin to destination. This ensures that assets are not only monitored over long distances but also managed more effectively through every step of the delivery process.
Use-Cases of RFID—at a Glance
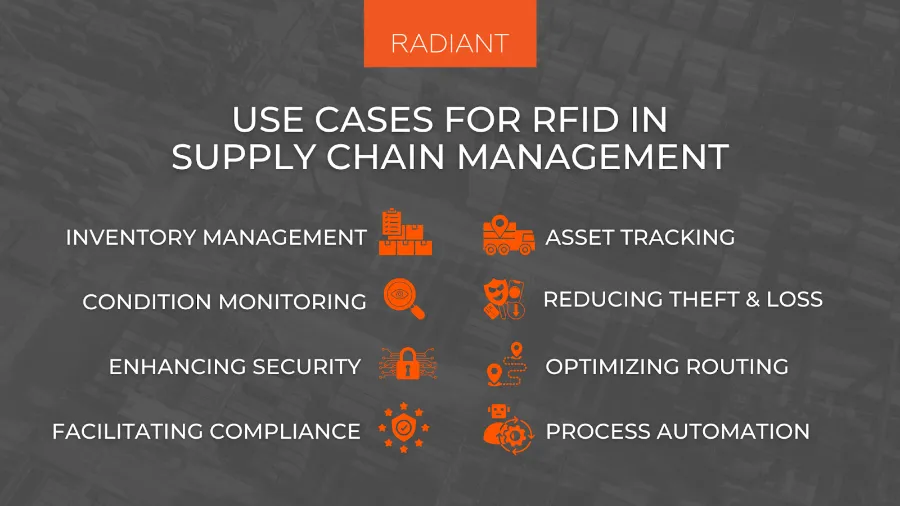
Source: Radiant RFID
Semi-passive RFID tags, also known as battery-assisted passive (BAP) tags, are equipped with a small battery that powers the tag's internal circuitry while relying on reader signals to initiate communication.
This hybrid approach enhances signal reliability and read range over passive tags, making them suitable for supply chain environments where direct reader contact is inconsistent.
They are predominantly used in industries like cold chain logistics, pharmaceuticals, and asset tracking that require enhanced data accuracy and environmental monitoring.
An example of their use is in temperature monitoring within the cold chain logistics sector. Semi-passive RFID tags can continuously monitor and log the temperature of sensitive goods, such as pharmaceuticals or perishable foods, throughout the transportation process.
Specialized RFID tags are custom-designed to meet specific requirements and environmental conditions within various sectors of the supply chain. These tags often feature unique functionalities, such as enhanced memory, ruggedization, or embedded sensors for temperature and humidity monitoring.
Industries such as agriculture, automotive, and aerospace frequently utilize specialized RFID tags to track and manage assets under extreme conditions or to monitor sensitive conditions throughout the supply chain.
One notable application is in the agriculture industry, where specialized RFID tags are used for livestock management. These tags can track the location and health data of animals, significantly improving herd management and disease control.
| Did you find this article helpful? Read these next! How to Calculate Canada Post Shipping Costs Warehouse Logistics: Everything You Need to Know What is Ecommerce Logistics? |
Having the right technology and support at every turn in your logistics operations is essential for Canadian businesses to stay competitive and profitable. Including RFID tags in your logistics solutions is a great way to gain clear visibility over your assets and inventory, reduce loss within your supply chain, and meet certain retailers requirements.
However, RFID can’t do everything and businesses still need a reliable, affordable, shipping partner to ensure your supply chain keeps everything moving as smoothly as possible. For Canadians, that means partnering with Ship Expert.
We’re an affordable shipping provider that helps Canadian businesses save up to 70% on shipping costs without volume minimums or monthly contracts.
To learn more about saving on shipping, contact the team at Ship Expert.

Director, Ship Expert
Greg Woo is a seasoned expert in the logistics and distribution industry, with a career spanning over two decades. He has a comprehensive understanding of shipping and distribution needs, and has extensive experience integrating with e-commerce stores as well as customer specific WMS (warehouse management systems) and ERP’s (enterprise resource planning software). His tenure in the industry and established courier and LTL partnerships have allowed clients to benefit from reduced shipping expenses, as well as improved operations through software and specialized integrations.
Greg is currently the Director at Ship Expert Inc., a role he has held since February 2015. Prior to his role at Ship Expert, Greg held significant positions at Juxto, a telecommunications and managed internet service provider.